
Your paper’s Introduction section should provide your readers with the information they need to grasp, appreciate, and build on the knowledge you present. Despite audience-dependent variations, the Introduction generally follows a four-part structure that sets the stage for the core of the paper. Check out annotated examples at the end to see how different authors have introduced their work.
| Contents |
| 1. Before your start 1.1. Identify your purpose 1.2. Analyze your audience 2. Writing your Introduction 2.1. General background: A broad opening 2.2. Specific background: Work done so far 2.3. Knowledge gap: Motivation for your work 2.4. Aim of your paper 3. Quick tips 4. Annotated examples |
The Introduction provides your audience with the background information necessary to understand the work you’re presenting in the article, and the reasons why you conducted your work. Therefore, clarify for yourself what problem you’re addressing and why your work is important.
Scientists in your specific field will probably understand your work’s motivation whether they read your Introduction or not. They might even skip the Introduction and focus on the Methods and Results. Outsiders are the people who will benefit most from a well-crafted Introduction. This is an opportunity for you to broaden their background knowledge and close the gap in technical knowledge.
Analyze papers from your target journal and follow the journal’s guidelines. This will inform the appropriate length and breadth for your Introduction, as well as the content needed to help your readers follow along. Let’s say you are writing a paper about CFD simulation in nuclear fission reactor. You can assume that readers of Physics of Fluids are interested in developments in fluid mechanics, but may not know much about reactor design. For other journals such as Nuclear Engineering and Design, readers will be nuclear science insiders.
If you are writing for a general audience, your Introduction will start with some broad, motivating background and fewer technical details. Below are excerpts from two journals articles. Although they describe the same research project, one is intended for a general audience (left) whereas the other is directed at scientists with previous knowledge on the topic (right).

Regardless of length, an effective Introduction resembles the first half of an abstract. Just like an abstract, one way to remember the different components is to visualize an hourglass: start with a broad opening and lead your reader toward the core of your paper.
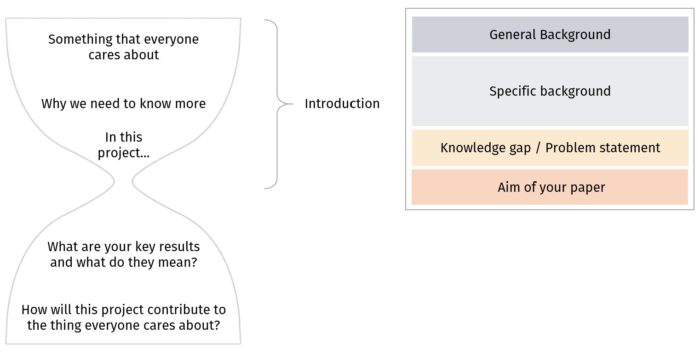
Here is an example illustrating our four-part structure (see more examples below).

The general background should demarcate the overall scientific setting of your work. Start with a general topic that everyone in your audience cares about. Note that the general background should give your audience a sense of what to expect from your paper, not an overview of the history of a field. Introduce only necessary background that is related to your work, and make sure it can narrow down to your thesis.
Give your reader a sense of previous accomplishments, current contradictions, and competing theories in the field. Cite previous work that illustrates your narrative and gives a balanced description of the scientific landscape on this research topic.
Give evidence of the incompleteness of the current understanding and of the value of investigating the field further. What is the gap that needs to be filled? Demonstrate the importance of this unsolved problem as the motivation for your work.
Finally, clearly state the aim and scope of this article (not the project) and what exact question is answered. You may also briefly explain how the study was conducted, and share a preview of your findings.
To get started or receive feedback on your draft, make an appointment with us. We’d love to help!
The point of an Introduction is to provide context for your work so readers understand its significance.
Xinyao “Anna” Liang
NSE Communication Fellow 2018-2021
View Profile
NSE students and postdocs: Want to talk with us about your project?
NSE Communication Lab: Room 24-216
nse-commlab@mit.edu
+1-617-253-3808
CommKit Content is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License 4.0 unless otherwise noted.